|
|
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| {{character | | {{character |
| |name=pi | | |name=pi |
| |script=North Italic Script
| |
| |sortform=20 | | |sortform=20 |
| |phoneme= | | |phoneme= |
| Line 7: |
Line 6: |
| |problem=Phonem | | |problem=Phonem |
| }} | | }} |
| == Commentary ==
| |
| Pi is one of the letters (together with [[index::L|Lambda]] and [[index::U|Upsilon]]) which serve as a basis for distinguishing the Magrè and Sanzeno alphabets (see [[index::Script]]): The variants {{c||P}}, {{c||P3}}, {{c||P4}}, {{c||P5}} with an angle (sometimes rounded), often termed "Venetoid" in the TIR, are attributed to the Magrè alphabet, while {{c||P2}} with a bar on top extending against writing direction is used in the Sanzeno alphabet.
| |
|
| |
|
| While the schibboleth letters mentioned above do usually appear in the expected forms and are grouped together appropriately in numerous inscriptions from both alphabetical contexts, the letter form ←{{c||L|d}} / {{c||L}}→ (commonly Magrè Lambda) does crop up in Sanzeno context, where it is not only incongruous, but in some cases must clearly be read {{p||p}} instead of {{p||l}}. We even have cases where all three forms ←{{c||P2|d}}, ←{{c||P2}}, ←{{c||L2}} (or turned the other way) appear together, being one clear (Sanzeno) Lambda, one clear (Sanzeno) Pi, and one letter of doubtful ascription.
| | Pi is one of the letters (together with [[index::L|lambda]] and [[index::U|upsilon]]) which serve as a basis for distinguishing the Magrè and Sanzeno alphabets (see [[index::Property:alphabet]] and [[index::Script]]): the variants {{c||P}}, {{c||P5}}, {{c||P3}}, {{c||P4}}, {{c||P6}} with an angle (sometimes rounded) belong to the Magrè alphabet, while {{c||P2}} with a single bar is the form used in the Sanzeno alphabet. |
|
| |
|
| ←{{c||P2|d}}, isolated (not accompanied by any other variant of Pi or Lambda), is read Pi based on content-related arguments in the inscriptions [[index::BZ-9]] and possibly [[index::NO-13]]. The name {{w||piθam(n)e|piθame}} in [[index::BZ-9]] is securely attested with anlauting {{p||p}} in [[index::Serso]] and [[index::Magrè]], but note another instance of the name written with ←{{c||P2|d}} in [[index::WE-3]] (see below). For the question of whether ←{{c||P2|d}} is intended in [[index::NO-13]], see the inscription page; if it is the case, {{w||perisna}} is well attested also. ←{{c||P2|d}} also appears on its own in [[index::NO-11]], but without parallel attestation no decision can be made between the readings {{w||liri}} and {{w||piri}}.
| | The Magrè forms with the angle, often termed "Venetoid" in TIR, are similar to forms of the Venetic alphabets (though {{c||P}} with a completely closed angle is not attested in the Venetic alphabets, which prefer opened variants like {{c||addP1}}). The variants with a small angle {{c||P}}, {{c||P5}} are used in the south. Particularly at Magrè, {{c||P}} has been and is sometimes still misread as rho (e.g., {{bib|MLR}}, {{bib|Markey 2006}}). The variants with a large angle {{c||P3}}, {{c||P4}}, which are used in the north, are even easier to confuse with rho (e.g., [[index::ST-2]]; however, in at least two instances ([[index::IT-4]] and [[index::IT-8]]) a gap between the lower ends of the hasta and the angled or curved line which forms the pocket can be clearly seen. {{c||P6}} occurs once in the north. |
|
| |
|
| ←{{c||P2|d}} appears combined with Sanzeno Lambda {{c||L2}} on [[index::CE-1.3]] (twice) and [[index::SZ-22.1]], and is consequently considered to represent Pi turned against writing direction in both cases. Both inscriptions duly have Sanzeno alphabet {{c||U2}}, though the one from geographically intermediate [[index::Cembra]] also features word-internal punctuation. With the bar of Pi extending in writing direction, the distinction between the three schibboleth letters Pi, Lambda and Upsilon is still sustained, and this system is actually the one in use in the Lugano alphabet. However, both inscriptions display Raetic features (←{{c||A}}, ←{{c||S}}).
| | Sanzeno pi {{c||P2}} is equivalent to the form prevalent in the Etruscan and Lepontic alphabets, and also sometimes used in Venetic. The letter occurs in more than thirty inscriptions and inscriptoids in alphabetic Sanzeno context. In ten certainly language-encoding inscriptions ([[index::CE-1.3]], [[index::SZ-15.1]], [[index::SZ-22.1]], [[index::SZ-30]], [[index::SZ-87]], [[index::SZ-98]], [[index::NO-11]], [[index::BZ-9]], [[index::BZ-10.1]], [[index::WE-3]]), thirteen tokens represent up to eight different types. Of these, two are attested in Magrè context with certain pi ({{w||piθam(n)e}} vel sim., {{w||piθie|pitie}} vel sim.). The letter can therefore be clearly identified as pi ({{bib|Salomon 2017}}: 245 f.). The letter {{c||P2|d}}, with the bar extending against writing direction, is still widely considered to be Sanzeno pi, but is better identified as a variant of tau (see [[index::T]]). On {{c||P2}} vs. {{c||P2|d}} in Sanzeno context, though with obsolete argumentation, see Salomon in {{bib|Kluge & Salomon 2015}}: 89–92. |
| | |
| It is not clear, how and why the non-Venetic features of the Sanzeno alphabet arose, but a letter variant ←{{c||P2|d}} might reasonably be expected to have been an intermediate form between {{c||P5}} and {{c||P2}}. However, on [[index::SZ-87]] ←{{c||P2|d}} appears combined with Sanzeno Pi {{c||P2}}. The two letters occur, separated by only one letter, within the same word {{c||S}}{{c||I}}{{c||P2}}{{c||I}}{{c||L}}, probably an individual name in the genitive. A reading Pi is nevertheless possible: The form might be compared with {{w||pipe}} on [[index::BZ-11]] (not autopsied!); [[index::SZ-15.1]], which also has {{c||L2}}, contains an individual name {{c||E}}{{c||I}}{{c||P2}}{{c||I}}{{c||P2|d}} with identical letter forms.
| |
| | |
| Three inscriptions have the triple combination of ←{{c||P2|d}}, ←{{c||P2}}, ←{{c||L2}}: the abovementioned [[index::WE-3]] and [[index::SZ-15.1]], as well as [[index::SZ-30]]. [[index::WE-3]] has three incontestably correct Sanzeno Lambdas, and one Sanzeno Pi in the name {{w||laspa}}, which is also attested on [[index::SZ-1.1]] and, incidentally, [[index::SZ-15.1]]. The dubious ←{{c||P2|d}} occurs in the name {{w||piθamnuale}}, as in [[index::BZ-9]] (above). [[index::SZ-15.1]] has one Sanzeno Lambda in {{w||laspa}}, two Sanzeno Pis in {{w||laspa}} and {{c||E}}{{c||I}}{{c||P2}}{{c||I}}{{c||P2|d}}, and two instances of ←{{c||P2|d}} in {{c||E}}{{c||I}}{{c||P2}}{{c||I}}{{c||P2|d}} and {{c||U4}}{{c||N}}{{c||U4}}{{c||Ś}}{{c||A5}}{{c||P2|d}}{{c||A5}}{{c||K}} (the latter sequence with a highly questionable parallel in [[index::SZ-14]] (with ←{{c||P2}})). [[index::SZ-30]], the only dextroverse one of the inscriptions discussed here, has Sanzeno Lambda twice in well attested forms, Sanzeno Pi in the anlaut of an isolated name (?) {{w||pumis}}, and twice anlauting {{c||P2}}→ in obscure words.
| |
| | |
| Regarding solely its form, the letter ←{{c||P2|d}} might in Sanzeno context be considered either an influence from the Magrè alphabet (Lambda, alongside Sanzeno Pi; in [[index::SZ-87]]), or a remnant form of Pi (alongside Sanzeno Lambda; in [[index::BZ-9]], [[index::CE-1.3]] and [[index::SZ-22.1]]). While it might not be absurd to postulate such a double origin of the form, neither of these explanations accounts for the cases where it appears alongside both regular Sanzeno letter forms. The postulation of writing mistakes is not advisable, seeing as there are three independent cases. In [[index::WE-3]], ←{{c||P2|d}} occurs only in the second line as opposed to ←{{c||P2}} in the first, which might be used as an argument for a scribal error, but in [[index::SZ-15.1]] they occur almost successively; in [[index::SZ-30]], the writer has switched back and forth, and that only in that part of the inscription which is left to us. Writing ←{{c||P2|d}} instead of ←{{c||P2}}, which is the only letter with a bar extending "backwards" from a straight hasta, may seem an easy mistake to make, but there appears to have been no problem with the equally counterintuitive ←{{c||A}}. Sigma is the only letter which is sometimes turned both ways in the same document (so in [[index::WE-3]]). All of the three inscriptions with the triple combination are noticably well and neatly executed specimens of some length.
| |
| | |
| Note that among twelve instances of ←{{c||P2|d}}, two words appear twice: the names {{w||piθam(n)e}} and {{w||pipie}}. The former might etymologically belong with other individual names in ''piθ-'', one of which is {{w||piθiave}}; one of the forms in question on [[index::SZ-30]] might also belong with this group. Yet it is unlikely that ←{{c||P2|d}} vs. {{c||P2}} reflects a phonetic reality – while a surprising number of characters for labial stops seem to have been used by the Raeti, and the problematic case of [[index::NO-13]] might connect ←{{c||P2|d}} with [[index::Φ|Φ5]], the name {{w||piθam(n)e}} is attested with regular Magrè Pi in [[index::Serso]].
| |
| | |
| In TIR, ←{{c||P2|d}} in Sanzeno context is consistently defined as Pi and transliterated accordingly. This includes fragmentary inscriptions which have not been discussed above ([[index::VN-2]], [[index::VN-3]], [[index::SZ-32]]), and a great number of inscriptoids from [[index::Sanzeno]] (most prominently the {{w||upi}}-inscriptions).
| |
|
| |
|
| {{bibliography}} | | {{bibliography}} |
Variants and attestation
Pi is one of the letters (together with lambda and upsilon) which serve as a basis for distinguishing the Magrè and Sanzeno alphabets (see Property:alphabet and Script): the variants 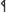 ,
, 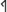 ,
, 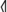 ,
, 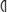 ,
, 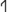 with an angle (sometimes rounded) belong to the Magrè alphabet, while
with an angle (sometimes rounded) belong to the Magrè alphabet, while 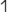 with a single bar is the form used in the Sanzeno alphabet.
with a single bar is the form used in the Sanzeno alphabet.
The Magrè forms with the angle, often termed "Venetoid" in TIR, are similar to forms of the Venetic alphabets (though 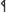 with a completely closed angle is not attested in the Venetic alphabets, which prefer opened variants like
with a completely closed angle is not attested in the Venetic alphabets, which prefer opened variants like 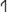 ). The variants with a small angle
). The variants with a small angle 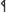 ,
, 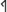 are used in the south. Particularly at Magrè,
are used in the south. Particularly at Magrè, 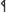 has been and is sometimes still misread as rho (e.g., MLR, Markey 2006). The variants with a large angle
has been and is sometimes still misread as rho (e.g., MLR, Markey 2006). The variants with a large angle 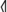 ,
, 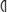 , which are used in the north, are even easier to confuse with rho (e.g., ST-2; however, in at least two instances (IT-4 and IT-8) a gap between the lower ends of the hasta and the angled or curved line which forms the pocket can be clearly seen.
, which are used in the north, are even easier to confuse with rho (e.g., ST-2; however, in at least two instances (IT-4 and IT-8) a gap between the lower ends of the hasta and the angled or curved line which forms the pocket can be clearly seen. 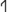 occurs once in the north.
occurs once in the north.
Sanzeno pi 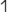 is equivalent to the form prevalent in the Etruscan and Lepontic alphabets, and also sometimes used in Venetic. The letter occurs in more than thirty inscriptions and inscriptoids in alphabetic Sanzeno context. In ten certainly language-encoding inscriptions (CE-1.3, SZ-15.1, SZ-22.1, SZ-30, SZ-87, SZ-98, NO-11, BZ-9, BZ-10.1, WE-3), thirteen tokens represent up to eight different types. Of these, two are attested in Magrè context with certain pi (piθam(n)e vel sim., pitie vel sim.). The letter can therefore be clearly identified as pi (Salomon 2017: 245 f.). The letter
is equivalent to the form prevalent in the Etruscan and Lepontic alphabets, and also sometimes used in Venetic. The letter occurs in more than thirty inscriptions and inscriptoids in alphabetic Sanzeno context. In ten certainly language-encoding inscriptions (CE-1.3, SZ-15.1, SZ-22.1, SZ-30, SZ-87, SZ-98, NO-11, BZ-9, BZ-10.1, WE-3), thirteen tokens represent up to eight different types. Of these, two are attested in Magrè context with certain pi (piθam(n)e vel sim., pitie vel sim.). The letter can therefore be clearly identified as pi (Salomon 2017: 245 f.). The letter 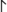 , with the bar extending against writing direction, is still widely considered to be Sanzeno pi, but is better identified as a variant of tau (see T). On
, with the bar extending against writing direction, is still widely considered to be Sanzeno pi, but is better identified as a variant of tau (see T). On 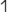 vs.
vs. 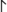 in Sanzeno context, though with obsolete argumentation, see Salomon in Kluge & Salomon 2015: 89–92.
in Sanzeno context, though with obsolete argumentation, see Salomon in Kluge & Salomon 2015: 89–92.
| Kluge & Salomon 2015
|
Sindy Kluge, Corinna Salomon, "Ausgewählte Funde aus Dercolo im Kontext der rätischen Inschriften", Wissenschaftliches Jahrbuch der Tiroler Landesmuseen 8 (2015), 80–95.
|
| Markey 2006
|
Thomas L. Markey, "Early Celticity in Slovenia and at Rhaetic Magrè (Schio)", Linguistica 46 (2006), 145–171.
|
![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() with an angle (sometimes rounded) belong to the Magrè alphabet, while
with an angle (sometimes rounded) belong to the Magrè alphabet, while ![]() with a single bar is the form used in the Sanzeno alphabet.
with a single bar is the form used in the Sanzeno alphabet.
![]() with a completely closed angle is not attested in the Venetic alphabets, which prefer opened variants like
with a completely closed angle is not attested in the Venetic alphabets, which prefer opened variants like ![]() ). The variants with a small angle
). The variants with a small angle ![]() ,
, ![]() are used in the south. Particularly at Magrè,
are used in the south. Particularly at Magrè, ![]() has been and is sometimes still misread as rho (e.g., MLR, Markey 2006). The variants with a large angle
has been and is sometimes still misread as rho (e.g., MLR, Markey 2006). The variants with a large angle ![]() ,
, ![]() , which are used in the north, are even easier to confuse with rho (e.g., ST-2; however, in at least two instances (IT-4 and IT-8) a gap between the lower ends of the hasta and the angled or curved line which forms the pocket can be clearly seen.
, which are used in the north, are even easier to confuse with rho (e.g., ST-2; however, in at least two instances (IT-4 and IT-8) a gap between the lower ends of the hasta and the angled or curved line which forms the pocket can be clearly seen. ![]() occurs once in the north.
occurs once in the north.
![]() is equivalent to the form prevalent in the Etruscan and Lepontic alphabets, and also sometimes used in Venetic. The letter occurs in more than thirty inscriptions and inscriptoids in alphabetic Sanzeno context. In ten certainly language-encoding inscriptions (CE-1.3, SZ-15.1, SZ-22.1, SZ-30, SZ-87, SZ-98, NO-11, BZ-9, BZ-10.1, WE-3), thirteen tokens represent up to eight different types. Of these, two are attested in Magrè context with certain pi (piθam(n)e vel sim., pitie vel sim.). The letter can therefore be clearly identified as pi (Salomon 2017: 245 f.). The letter
is equivalent to the form prevalent in the Etruscan and Lepontic alphabets, and also sometimes used in Venetic. The letter occurs in more than thirty inscriptions and inscriptoids in alphabetic Sanzeno context. In ten certainly language-encoding inscriptions (CE-1.3, SZ-15.1, SZ-22.1, SZ-30, SZ-87, SZ-98, NO-11, BZ-9, BZ-10.1, WE-3), thirteen tokens represent up to eight different types. Of these, two are attested in Magrè context with certain pi (piθam(n)e vel sim., pitie vel sim.). The letter can therefore be clearly identified as pi (Salomon 2017: 245 f.). The letter ![]() , with the bar extending against writing direction, is still widely considered to be Sanzeno pi, but is better identified as a variant of tau (see T). On
, with the bar extending against writing direction, is still widely considered to be Sanzeno pi, but is better identified as a variant of tau (see T). On ![]() vs.
vs. ![]() in Sanzeno context, though with obsolete argumentation, see Salomon in Kluge & Salomon 2015: 89–92.
in Sanzeno context, though with obsolete argumentation, see Salomon in Kluge & Salomon 2015: 89–92.